Polyolefin foam insulation has gained attention in the construction and manufacturing sectors. This material provides excellent thermal performance, making it a favorite for energy efficiency. Reports indicate that polyolefin foam insulation can reduce heating and cooling costs by up to 30%. In times of rising energy prices, such savings become critical.
Moreover, this insulation type is lightweight yet durable. It resists moisture and does not attract mold, which enhances its suitability for various environments. Construction industry studies show that materials like polyolefin foam insulation contribute to improved building sustainability. However, not all applications utilize it effectively, revealing a gap in knowledge and best practices among builders.
Despite its advantages, some still question the long-term performance of polyolefin foam insulation. It is essential to address these doubts with further research and education. Understanding this material's properties can lead to better insulation solutions in a rapidly evolving market. As companies strive for greener practices, the potential of polyolefin foam insulation deserves attention and exploration.

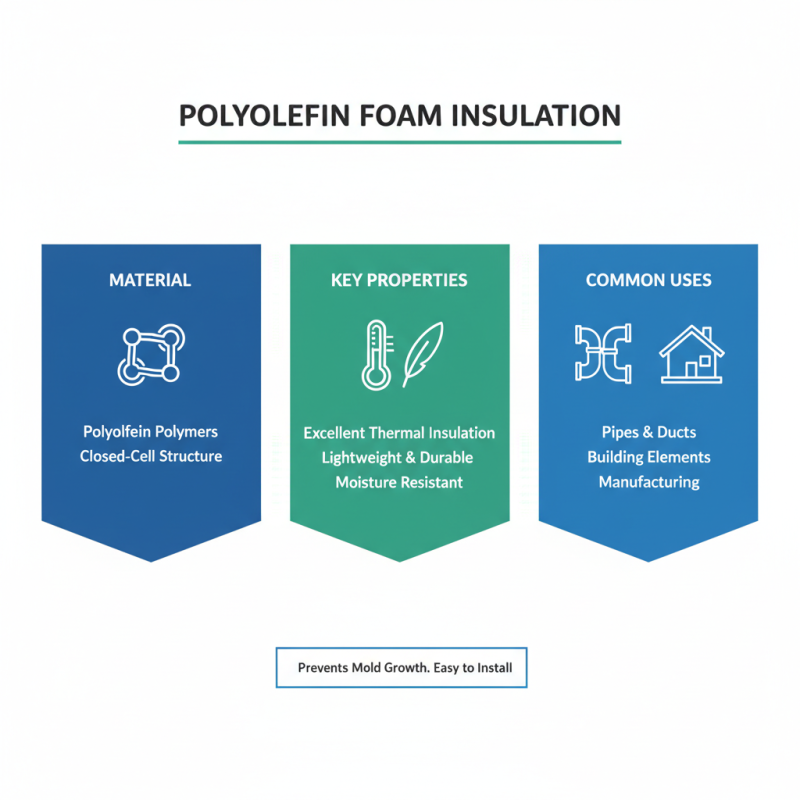
Polyolefin foam insulation is an innovative material used widely in construction and manufacturing. It is made from polyolefin polymers, which provide excellent thermal insulation properties. This foam is lightweight yet durable, making it easy to install. It is often used to insulate pipes, ducts, and other building elements. The closed-cell structure of polyolefin foam keeps moisture out, preventing mold growth.
One significant advantage of this type of insulation is its resistance to chemicals. It can withstand exposure to many substances without degrading. This makes it suitable for use in various environments, including industrial settings. Its energy efficiency can lead to significant savings on heating and cooling bills. However, some users have reported issues with availability and cost.
Polyolefin foam insulation is also flexible and can be molded to fit irregular shapes. This adaptability allows for comprehensive coverage of a space. While it offers many benefits, potential users need to research different options. Testing the insulation in real-world applications can reveal strengths and weaknesses. Each project may present unique challenges, and adjustments might be necessary.
Polyolefin foam insulation is gaining popularity due to its unique characteristics. These materials are lightweight and flexible, making them easy to handle and install. They offer excellent thermal and acoustic insulation. According to a recent industry report, polyolefin foams can achieve thermal conductivity values as low as 0.030 W/m·K. This performance makes them suitable for various applications, including HVAC systems and building insulation.
One key characteristic of polyolefin foam is its resistance to moisture. This feature prevents mold growth and enhances indoor air quality. Additionally, polyolefin foams are chemically resistant. They can withstand exposure to many harsh chemicals without degrading. This durability increases their lifespan and reduces maintenance costs.
Tips: When selecting insulation materials, consider the environmental impact. Polyolefin is often recyclable, reducing landfill waste. Always verify the insulation values to ensure efficiency.
Another aspect to consider is the manufacturing process. While polyolefin foam production is efficient, quality can vary significantly. Not all products meet the same standards. Thus, thorough research is essential to find reliable options. Don't overlook product specifications. Small details can lead to significant differences in performance.
| Characteristic | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Polyolefin foam provides superior thermal resistance, reducing heat transfer. | Energy savings and improved comfort in buildings. |
| Moisture Resistance | Highly resistant to moisture, preventing mold and mildew growth. | Longer lifespan of insulation and reduced health risks. |
| Lightweight | Lightweight material for easier handling and installation. | Lower shipping costs and easier project execution. |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to various chemicals, making it suitable for industrial applications. | Versatile use in different environments without degradation. |
| Sound Absorption | Effective sound dampening properties. | Improved acoustic performance in buildings and spaces. |
When comparing polyolefin foam to traditional insulation materials, distinct differences emerge. Polyolefin foam is lightweight and flexible. This makes it easier to handle during installation. Traditional insulations, like fiberglass or foam board, can be bulky and heavy. They may require special tools for cutting and fitting, complicating the installation process.
Polyolefin foam also boasts superior moisture resistance. This is a key factor in preventing mold growth. Traditional insulations often absorb water, losing their effectiveness. However, some types of traditional insulation offer better soundproofing. This could be a crucial consideration in noisy environments. The choice between these materials should depend on specific needs, like water exposure and sound control.
Cost is another aspect worth discussing. Polyolefin foam might have a higher upfront cost. Yet, it can provide long-term savings due to its energy efficiency. Traditional options may appear cheaper but can lead to increased energy bills. It’s essential to weigh short-term savings against long-term benefits. Consumers should carefully evaluate their building's requirements before making a decision.
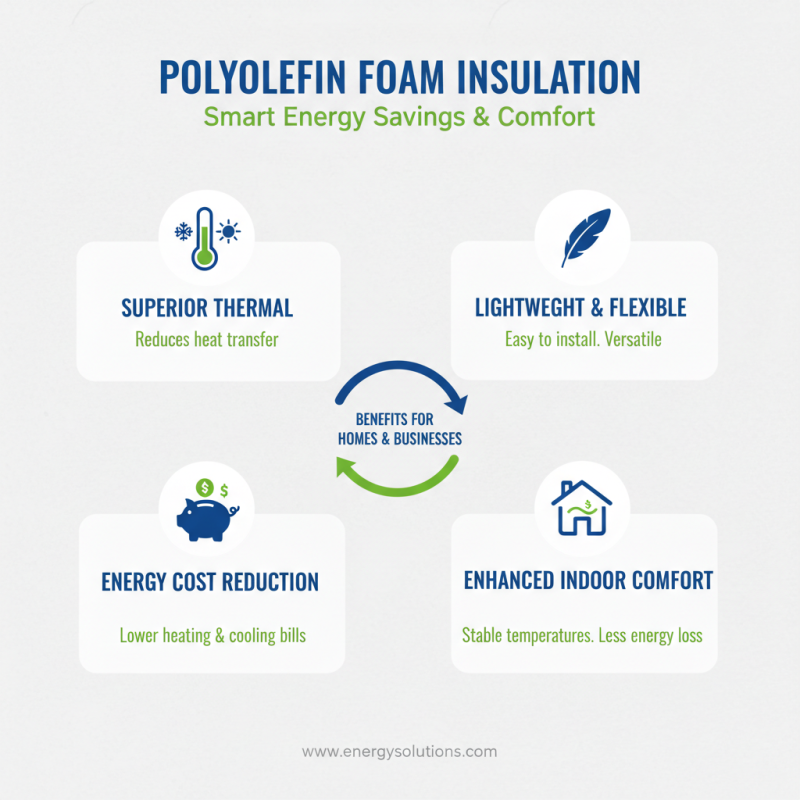
Polyolefin foam insulation is a versatile material known for its excellent thermal performance. It is lightweight and flexible, making it suitable for various applications. This insulation type helps reduce energy loss in buildings, translating to significant savings on heating and cooling costs. Homes and businesses can benefit from its effectiveness in creating a comfortable indoor environment with minimal energy expenditure.
One major energy efficiency benefit of using polyolefin foam insulation is its resistance to moisture. This feature prevents mold and mildew growth, which can disrupt energy performance. The insulation traps heat in winter and keeps spaces cool in summer, enhancing year-round comfort. However, it’s worth noting that improper installation can lead to air gaps, reducing its effectiveness.
Choosing the right thickness is also critical. If it’s too thin, you might not achieve the desired efficiency. If it’s too thick, it could be unnecessary for your specific climate. The right balance is essential. Don’t overlook these details when considering polyolefin foam insulation. By making informed choices, you can maximize energy efficiency while ensuring sustainability.
Polyolefin foam insulation is versatile and widely used across various industries. Its lightweight and flexible nature makes it ideal for automotive and construction applications. In the automotive industry, it is commonly used for thermal and acoustic insulation.
According to a recent report by the International Energy Agency, polyolefin foam can reduce vehicle weight, improving fuel efficiency by up to 5%. This is crucial as manufacturers aim to meet stricter emissions regulations.
In construction, polyolefin foam is employed in walls, roofs, and floors to enhance energy efficiency. The U.S. Department of Energy states that using such insulation can lower energy bills by 20-30%. However, some challenges persist. While the foam is water-resistant, prolonged exposure to moisture can diminish its effectiveness. Additionally, its production involves the use of energy-intensive processes, raising concerns about environmental sustainability.
Despite these drawbacks, the expanding energy sector continues to embrace polyolefin foam for its thermal properties, providing a pathway for innovation and improvement in insulation techniques.






Scan QR code to download the app
LSP Products was founded by plumbers over 50 years ago with a focus on unparalleled innovation, superior product quality, and best-in-class service to the plumbing industry. Our primary focus is the new construction market where we develop products that make installations easy and provide significant cost savings to the plumbing/mechanical contractor. LSP has a manufacturing facility located in Monterrey, Mexico and a distribution center in Dallas, Texas. We are proud to offer many products designed and made in North America… About LSP
Submit the form below to receive the document via email.



